Domain: Car Track. More...
#include <domain.h>
Inheritance diagram for car_track::CarTrack:
Public Member Functions | |
| size_t | inputs () const override |
| Number of inputs to a Brain. | |
| size_t | outputs () const override |
| Number of outputs from a Brain. | |
| bool | evaluatePopulation (darwin::Population *population) const override |
| Assigns fitness values to every genotype. More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from darwin::Domain Public Member Functions inherited from darwin::Domain | |
| virtual unique_ptr< core::PropertySet > | calibrateGenotype ([[maybe_unused]] const Genotype *genotype) const |
| Optional: additional fitness metrics (normally not used in the population evaluation, ie a test set) | |
Detailed Description
Domain: Car Track.
Race around a procedurally generated track, using the car's sensors (camera, ...)
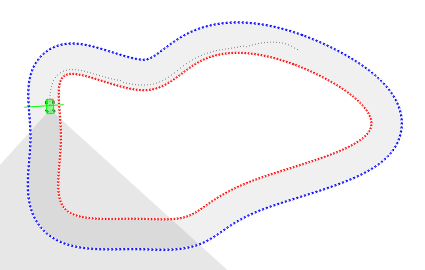
Inputs
- Camera: the color (and optionally depth) channels from the drone's camera
- Touch sensor (optional)
- Compass (optional)
- Accelerometer (optional)
Outputs
| Output | Value |
|---|---|
| 0 | acceleration force (negative values result in reverse movement) |
| 1 | desired steering angle (-1.0 .. +1.0) |
Member Function Documentation
◆ evaluatePopulation()
|
overridevirtual |
Assigns fitness values to every genotype.
Having a good fitness function is a key part of evolutionary algorithms:
- Perhaps obvious, the fitness value should accurately estimate the quality of a particular solution
- A "smooth" distribution is preferable since it provides a gradient which can guide the incremental search in the solutions space. (ex. if most fitness values are 1.0 or 0.0 it's hard to know which genotypes are good candidates for reproduction)
- Returns
trueif the evolution goal was reached
Implements darwin::Domain.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- C:/Users/lemo/work/darwin/domains/car_track/domain.h
- C:/Users/lemo/work/darwin/domains/car_track/domain.cpp
 1.8.14
1.8.14